|
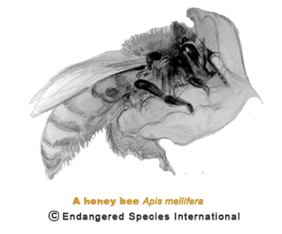
Bees include about 30,000 species. Most are solitary in behavior but roughly 1,000 have an advanced social behavior. Honey bee is one of the four distinct species in the genus Apix and it is the most known social bee.
A worker honey bee stays inside the hive for about three weeks before becoming an active forager. The tasks of the bee in the hive changes as the bee gets older. For the remaining one to three weeks of her life after she leave the hive, she collects nectar and pollen from flowers. Plant resins are also gathered to consolidate the hive.
Most crops (about 70 percent) that are used today require pollination to develop fruits, nuts, and seeds. It is estimated that those crops account for one trillion dollars in annual sales of agriculture products around the globe. Examples of common crops depending on bee pollination include broccoli, blueberry, cherry, apple, and cucumbers.
Since wild insects have decline worldwide mostly in part due to habitat destruction and pesticide use, farmers use the European bee for pollination. The European bee can be transported in boxes caring thousands of bees from crop to crop.
Many countries around the world have documented a great decline in the number of bee populations including China, Brazil, North America, and Europe. The reasons of such troubling decline is not really known but pesticides (e.g.,Imidacloprid), poor nutrition, viruses, parasite varroa mite, and stress are often mentioned as the likely causes. At the same time, beekeepers are scrambling to keep vegetables and fruits as abundant as they used to be.
Pollinators like bees have always been taking for granted but until recently we finally realize that preserving bees and other pollinators is essential for our economies that deeply depend on them.
Continue on page 7
|
|
|









